If you’re planning to start an online business, understanding the different types of e commerce is not just helpful—it’s absolutely essential. The digital marketplace is vast and dynamic, and choosing the right model can mean the difference between scalable growth and missed opportunities.
In this article, we’ll explore the 7 powerful types of e commerce, why they matter, and how to choose the right path for your business. Whether you’re an entrepreneur launching a new store or a traditional business shifting online, this guide will help you get started on the right foot.
What is E-Commerce?
At its core, e-commerce (short for electronic commerce) refers to buying and selling goods or services over the internet. This can range from physical products to digital services, and it encompasses all kinds of business transactions—retail, wholesale, services, and more.
But not all e-commerce is the same. In fact, there are multiple ecommerce types, each with its own advantages, challenges, and ideal use cases.
Why Understanding the Types of E-Commerce Matters
Before building your online store or choosing an e-commerce platform, it’s crucial to understand the category of e-commerce your business will fall under. This decision affects:
-
Your website design
-
Marketing strategy
-
Inventory management
-
Payment systems
-
Customer experience
And of course, your ability to grow and scale effectively.
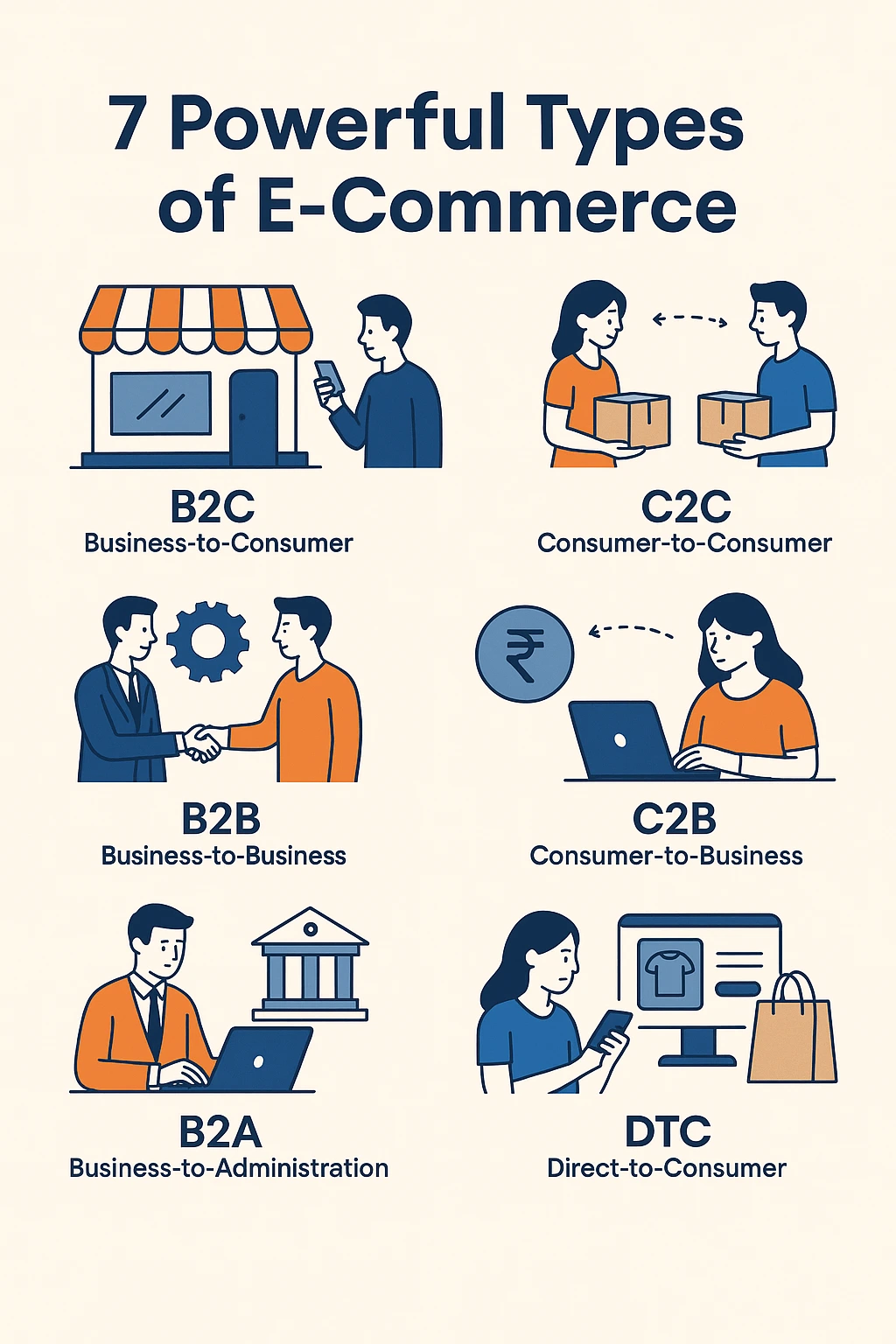
The 7 Most Powerful Types of E-Commerce
Let’s dive into the 7 main types of e commerce you should know about:
1. Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
Definition: Businesses sell directly to individual customers.
Examples: Amazon, Flipkart, Myntra
Best for: Retailers, DTC brands, lifestyle and fashion products
Why it matters: B2C is the most popular form of e-commerce. With a strong focus on user experience, product quality, and marketing, businesses can thrive by connecting directly with their target market.
2. Business-to-Business (B2B)
Definition: Businesses sell products or services to other businesses.
Examples: Alibaba, IndiaMART, Salesforce
Best for: Wholesale distributors, manufacturers, SaaS companies
Why it matters: B2B e-commerce typically involves higher order values, longer buying cycles, and deeper relationships. Your website must be tailored to professional buyers.
3. Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C)
Definition: Consumers sell directly to other consumers.
Examples: eBay, OLX, Facebook Marketplace
Best for: Used goods, collectibles, homemade products
Why it matters: C2C platforms enable individuals to monetize their unused or handmade items. Building trust between users is key in this model.
4. Consumer-to-Business (C2B)
Definition: Individuals offer products or services to businesses.
Examples: Fiverr, Upwork, influencer collaborations
Best for: Freelancers, influencers, consultants
Why it matters: The gig economy is booming. C2B gives professionals the chance to monetize skills, content, and influence.
5. Business-to-Administration (B2A)
Definition: Businesses provide goods or services to government bodies or public institutions.
Examples: Legal services, tax filing tools, cybersecurity solutions for government
Best for: Niche service providers, consultants
Why it matters: While not as mainstream, B2A e-commerce is lucrative and often long-term, especially for specialized services.
6. Consumer-to-Administration (C2A)
Definition: Consumers interact and make payments to the government online.
Examples: Paying taxes, applying for licenses, government services
Best for: Public service platforms, finance tech tools
Why it matters: C2A simplifies civic services. While not revenue-generating, it’s vital for user engagement and utility.
7. Direct-to-Consumer (DTC)
Definition: Manufacturers or producers sell directly to consumers, bypassing traditional retail channels.
Examples: Warby Parker, BoAt, Mamaearth
Best for: Brands looking for full control over the customer journey
Why it matters: DTC brands own the entire customer experience—from product creation to final sale. It’s personal, scalable, and data-rich.
Choosing the Right Type for Your Business
Every business is unique, and there’s no one-size-fits-all approach. Here’s how to determine the best types ecommerce model for you:
-
Product Type: Are you selling physical goods, digital products, or services?
-
Target Audience: Are you targeting businesses, consumers, or public institutions?
-
Sales Strategy: Do you want volume sales, personalized services, or long-term contracts?
-
Platform Needs: Do you need a complex wholesale portal or a simple, attractive online store?
Real-World Success Starts with the Right Website
Regardless of the ecommerce and types you choose, a professional and optimized website is your foundation. A poorly designed site can turn away customers even before you make your first sale.
That’s why businesses across India turn to GegoSoft’s website design services. Their team understands not only how to build a website but how to create a seamless e-commerce experience that converts visitors into loyal customers.
Planning to build a WooCommerce store? GegoSoft also specializes in WooCommerce website development—perfect for B2C, DTC, or even subscription-based models.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the types of e commerce models isn’t just academic—it’s strategic. The right category sets the tone for your operations, branding, and success.
Whether you’re just starting or scaling an existing business, knowing your ecommerce types helps you avoid mistakes, reach the right customers, and build long-term value.
And remember—your online presence starts with a strong website. Build smart. Grow faster. Choose wisely.
Want help building your online store?
Start with a free consultation from GegoSoft’s expert developers and turn your e-commerce idea into a revenue-generating reality.